
- #ITIL INCIDENT PRIORITY MATRIX HOW TO#
- #ITIL INCIDENT PRIORITY MATRIX OFFLINE#
#ITIL INCIDENT PRIORITY MATRIX OFFLINE#
If the ITIL Assessment illustrates a weakness in logging Incidents, it will show that IT members see a CI down or offline and put the fix in without logging an Incident or recording a Change. For example, most organizations do well in all but two or three process activities: Logging, Classification, and Prioritization. If we measure the standardized outcomes of each process activity through the consistent usage of a questionnaire, we will soon find out which ones the organization performs better – or worse – than expected. This needs to happen as soon as a workaround is established, and the users are no longer impacted. Closure – Closing the Incident in the ITSM tool.Resolution and Recovery – The Incident Management process’s goal is to resolve the Incident as quickly as possible.At times, one small CI is reported down, and an Incident is raised only to find out that it is dependent on a more significant CI, also down.
#ITIL INCIDENT PRIORITY MATRIX HOW TO#
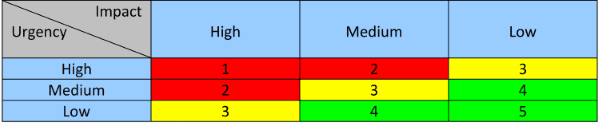
Investigation and Diagnosis – Investigating what is really down and how to resolve the Incident. Escalation – Escalating the Incident in one of two ways (Functional and Hierarchical). Initial Diagnosis – Do we have a quick diagnosis?. Prioritization – Assessing a priority for the Incident using the Priority Matrix. Classification – Classifying the Incident using predefined classes. Logging – Logging the Incident into an ITSM tool. Identification – Identifying a Configuration Item (CI) is – or soon will be – down. For example, most organizations use a basic Incident Management process (or practice in ITIL4) with the following activities: The maturity of an entire process may be broken down into the process activity subcategories. If we think back to ITIL basics, each method has “process activities” used to carry out a given function. Most ITIL Assessments will evaluate the ITIL process to see where they rate against the five levels above. ITIL Incident Management Process Maturity The goal is to optimize against a greater purpose. This could include automation and integration with non-IT processes and multiple toolsets. We need to re-focus the direction from process execution to optimization of the process for future iterations. Maturity Level 5 – Optimizing – Once we move toward Level 5, we make significant data-based decisions. Also, these same metrics may be established for projects and programs. Leadership leverages process KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and CSFs (Critical Success Factors) to evaluate a process’s health. Maturity Level 4 – Quantitatively Managed – As an organization moves toward Level 4, decisions are based on quantifiable data. Maturity Level 3 – Defined – Process inputs and outputs are defined, training established, metrics established, the level of risk is understood, and processes are audited. 
Maturity Level 2 – Managed – Processes are established, and the work is loosely managed, just not executed in a standardized, repeatable manner.Many organizations will baseline their maturity at Level 1 as they begin their process-maturity journey. Maturity Level 1 – Initial – There is no documented and adhered to process.
The CMMI model has five levels: CMMI Maturity Levels

Most ITIL assessments are based on the CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) model.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
